本文作者:chenssy
出处:http://cmsblogs.com/?p=4036
在学习
Spring源码的过程中发现的好站+好贴,原创不易感谢作者。Spring版本:Spring 5.0.6.RELEASE
前面的文章都是基于 BeanFactory 这个容器来进行分析的,BeanFactory 容器有点儿简单,并不适用于我们生产环境,在生产环境我们通常会选择 ApplicationContext ,相对于大多数人而言,它才是正规军,相比于 BeanFactory 这个杂牌军而言,它由如下几个区别:
- 继承 MessageSource,提供国际化的标准访问策略。
- 继承 ApplicationEventPublisher ,提供强大的事件机制。
- 扩展 ResourceLoader,可以用来加载多个 Resource,可以灵活访问不同的资源。
- 对 Web 应用的支持。
ApplicationContext
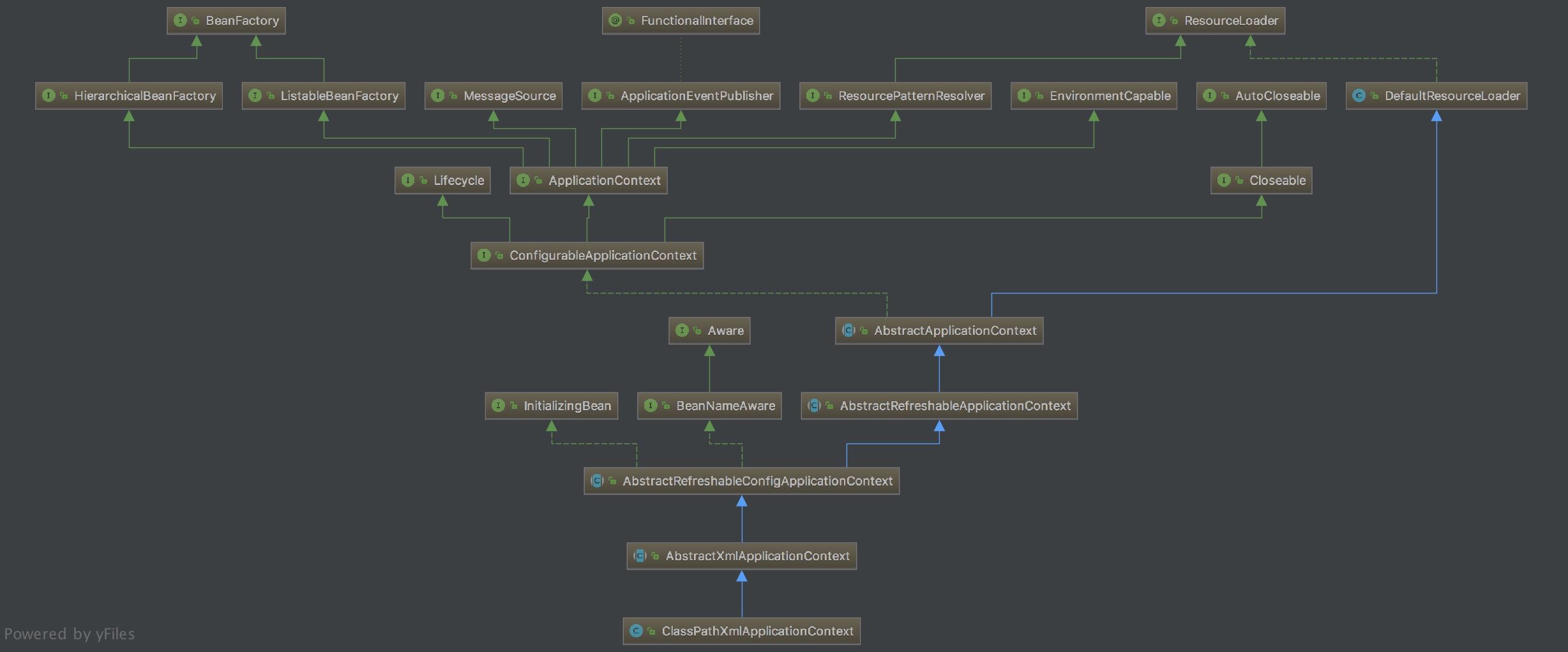
下图是 ApplicationContext 结构类图:
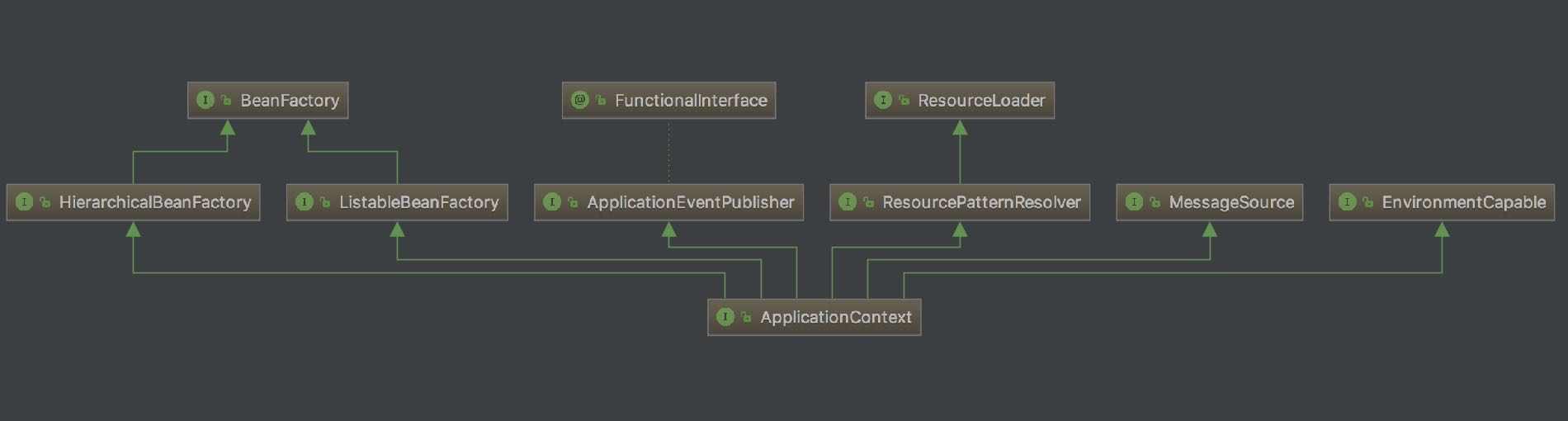
BeanFactory:Spring 管理 Bean 的顶层接口,我们可以认为他是一个简易版的 Spring 容器。
ApplicationContext 继承 BeanFactory 的两个子类:HierarchicalBeanFactory 和 ListableBeanFactory。HierarchicalBeanFactory 是一个具有层级关系的 BeanFactory,拥有属性 parentBeanFactory。ListableBeanFactory 实现了枚举方法可以列举出当前 BeanFactory 中所有的 bean 对象而不必根据 name 一个一个的获取。
ApplicationEventPublisher:用于封装事件发布功能的接口,向事件监听器(Listener)发送事件消息。
ResourceLoader:Spring 加载资源的顶层接口,用于从一个源加载资源文件。
ApplicationContext 继承 ResourceLoader 的子类 ResourcePatternResolver,该接口是将 location 解析为 Resource 对象的策略接口。
MessageSource:解析 message 的策略接口,用不支撑国际化等功能。
EnvironmentCapable:用于获取 Environment 的接口。
ApplicationContext 的子接口
ApplicationContext 有两个直接子类:WebApplicationContext 和 ConfigurableApplicationContext。
WebApplicationContext
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext { |
该接口只有一个 getServletContext() ,用于给 servlet 提供上下文信息。
ConfigurableApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable { |
从上面代码可以看到 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口提供的方法都是对 ApplicationContext 进行配置的,例如 setEnvironment()、addBeanFactoryPostProcessor,同时它还继承了如下两个接口:
- Lifecycle:对 context 生命周期的管理,它提供
start()和stop()方法启动和暂停组件。 - Closeable:标准 JDK 所提供的一个接口,用于最后关闭组件释放资源等。
WebApplicationContext 接口和 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口有一个共同的子类接口 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,该接口将这两个接口进行合并,提供了一个可配置、可管理、可关闭的WebApplicationContext,同时该接口还增加了 setServletContext(),setServletConfig()等方法,用于装配WebApplicationContext。
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext { |
上面三个接口就可以构成一个比较完整的 Spring 容器,整个 Spring 容器体系涉及的接口较多,所以下面小编就一个具体的实现类来看看 ApplicationContext 的实现(其实在前面一系列的文章中,小编对涉及的大部分接口都已经分析了其原理),当然不可能每个方法都涉及到,但小编会把其中最为重要的实现方法贴出来分析。
ApplicationContext 的实现类较多,就以 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 来分析 ApplicationContext。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 是我们在学习 Spring 过程中用的非常多的一个类,很多人第一个接触的 Spring 容器就是它,包括小编自己,下面代码我想很多人依然还记得吧。
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); |
下图是 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的结构类图:
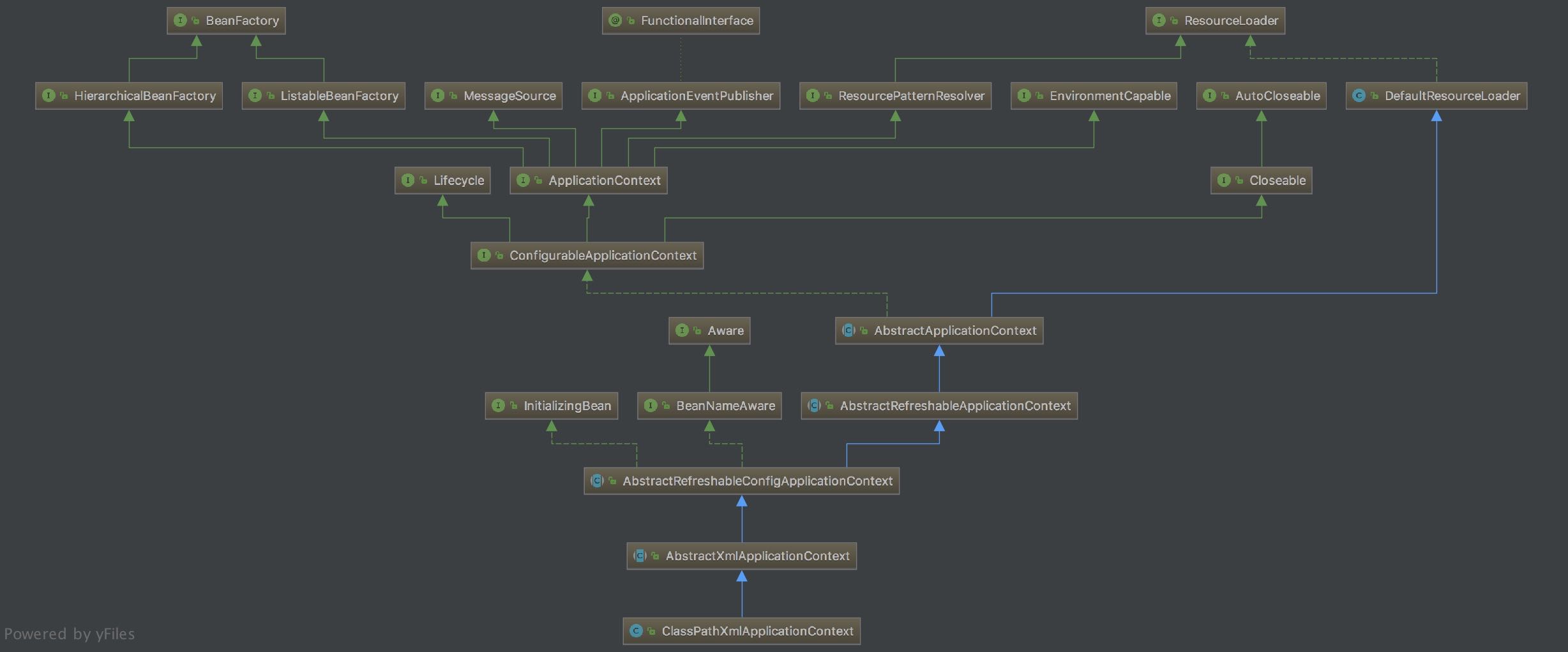
主要的的类层级关系如下:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext |
这种设计是模板方法模式典型的应用,AbstractApplicationContext 实现了 ConfigurableApplicationContext 这个全家桶接口,其子类 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 又实现了 BeanNameAware 和 InitializingBean 接口。所以 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 设计的顶级接口有:
BeanFactory:Spring 容器 Bean 的管理MessageSource:管理 message ,实现国际化等功能ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发布ResourcePatternResolver:资源加载EnvironmentCapable:系统 Environment(profile + Properties) 相关Lifecycle:管理生命周期Closeable:关闭,释放资源InitializingBean:自定义初始化BeanNameAware:设置 beanName 的 Aware 接口
下面就这些接口来一一分析。
MessageSource
MessageSource 定义了获取 message 的策略方法 getMessage(),在 ApplicationContext 体系中,该方法 AbstractApplicationContext 实现,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中,它持有一个 MessageSource 实例,将 getMessage() 的实现给该实例来实现,如下:
private MessageSource messageSource; |
真正实现 是在 AbstractMessageSource 中,如下:
public final String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String defaultMessage, Locale locale) { |
具体的实现这里就不分析了。
ApplicationEventPublisher
用于封装事件发布功能的接口,向事件监听器(Listener)发送事件消息。
该接口提供了一个 publishEvent() 用于通知在此应用程序中注册的所有的监听器。
该方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中实现。
|
如果指定的事件不是ApplicationEvent,则它将包装在PayloadApplicationEvent中。如果存在父级 ApplicationContext ,则同样要将 event 发布给父级 ApplicationContext。
ResourcePatternResolver
ResourcePatternResolver 接口继承 ResourceLoader 接口,为将 location 解析为 Resource 对象的策略接口。他提供的 getResources() 在 AbstractApplicationContext 中实现,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中他持有一个 ResourcePatternResolver 的实例对象。
如下:
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { |
如果小伙伴对 Spring 的 ResourceLoader 比较熟悉的话,你会发现最终是在 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 中实现,该类是 ResourcePatternResolver 接口的实现者。
EnvironmentCapable
提供当前系统环境 Environment 组件。提供了一个 getEnvironment() 用于返回 Environment 实例对象,该方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 实现。
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() { |
如果持有的 environment 实例对象为空,则调用 createEnvironment() 创建一个。
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() { |
StandardEnvironment 是一个适用于非 WEB 应用的 Environment。
Lifecycle
一个用于管理声明周期的接口。
在 AbstractApplicationContext 中存在一个 LifecycleProcessor 类型的实例对象 lifecycleProcessor,AbstractApplicationContext 中关于 Lifecycle 接口的实现都是委托给 lifecycleProcessor 实现的。如下:
|
在启动、停止的时候会分别发布 ContextStartedEvent 和 ContextStoppedEvent 事件。
Closeable
Closeable 接口用于关闭和释放资源,提供了 close() 以释放对象所持有的资源。在 ApplicationContext 体系中由AbstractApplicationContext 实现,用于关闭 ApplicationContext 销毁所有 bean ,此外如果注册有 JVM shutdown hook,同样要将其移除。如下:
public void close() { |
调用 doClose() 发布 ContextClosedEvent 事件,销毁所有 bean(单例),关闭 BeanFactory 。如下:
protected void doClose() { |
InitializingBean
InitializingBean 为 bean 提供了初始化方法的方式,它提供的 afterPropertiesSet() 用于执行初始化动作。在 ApplicationContext 体系中,该方法由 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 实现,如下:
public void afterPropertiesSet() { |
执行 refresh() ,该方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中执行,执行整个 Spring 容器的初始化过程。该方法将在下篇文章进行详细分析说明。
BeanNameAware
设置 bean name 的接口。接口在 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 中实现。
public void setBeanName(String name) { |
由于篇幅问题再加上大部分接口都已经在前面文章进行了详细的阐述,所以本文主要是以 Spring Framework 的 ApplicationContext 为中心,对其结构和功能的实现进行了简要的说明。
这里不得不说 Spring 真的是一个非常优秀的框架,具有良好的结构设计和接口抽象,它的每一个接口职能单一,且都是具体功能到各个模块的高度抽象,且几乎每套接口都提供了一个默认的实现(defaultXXX)。
对于 ApplicationContext 体系而言,他继承 Spring 中众多的核心接口,能够为客户端提供一个相对完整的 Spring 容器,接口 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对 ApplicationContext 接口再次进行扩展,提供了生命周期的管理功能。
抽象类 ApplicationContext 对整套接口提供了大部分的默认实现,将其中“不易变动”的部分进行了封装,通过“组合”的方式将“容易变动”的功能委托给其他类来实现,同时利用模板方法模式将一些方法的实现开放出去由子类实现,从而实现“**对扩展开放,对修改封闭**”的设计原则。
最后我们再来领略下图的风采: